Pedigree Analysis Chart
Genetic counselling involves obtaining detailed family history of individual or couple to assess the risk of transmission of a particular genetic condition to their next generation or offspring. Genetic counsellor educates you and your family how a particular genetic problem is inherited to their offspring. Genetic counsellor helps you understand whether any genetic problem is being inherited in your family. Counsellor will help you decide what type of genetic test needs to be done.
Genetic counselling is generally recommended when you are planning a pregnancy, where couple were identified with recurrent pregnancy loss, couple have a family history of particular clinical condition, history of neonatal deaths in the family, previous child affect with a birth defect. Genetic counselling for adults is usually recommended in specific area like hereditary breast cancer, cardiovascular problems, facing with any neurological problems, etc.,
As a part of genetic counselling, the counsellor collects family history of the individual or couple and prepares a diagram that represents the occurrence of a phenotype in each generation. Pedigree chart uses certain symbols to represent male and female, particular genetic condition whether he or she is a carrier or affected.
Pedigree analysis will helps to identify different how a genetic condition is getting inherited in the family, there are different types hereditary patterns that helps genetic counsellor identify what type of genetic test will benefit the individual.
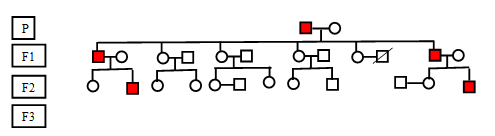
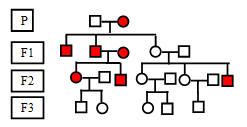
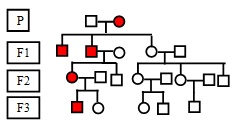
Autosomal Dominant inheritance: It is condition in which every generation in the family will have an affected individual. Affected offspring will always have affected parent. In autosomal inheritance both males and females are equally affected.
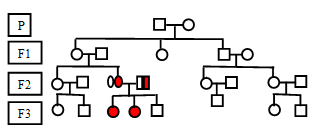
Autosomal Recessive inheritance: It is a condition in which not every generation in the family will have an affected individual, it skips a generation. Unlike autosomal dominant the affected offspring will not have an affected parent. In this condition the parents are likely to be carriers for particular genetic condition. In recessive inheritance also both males and females are equally affected.
Y- linked inheritance: It is similar to dominant inheritance, where every generation is affected. In this condition only males are affected females are not affected as the Y chromosome is transmitted to males rather than females. All affected fathers will transmit the disease to his sons.
X Linked recessive inheritance: In this condition both males and females are affected, but there are more chances of males getting affected rather female, because they carry another X chromosome from father which might be normal. In this recessive condition son gets affected but mother is normal. For a daughter to be affected father should be affected, mother should be carrier or affected. Like autosomal recessive inheritance X linked recessive inheritance can also skip a generation.
X Linked autosomal inheritance: Like autosomal dominant inheritance X linked dominant inheritance cannot skip a generation. All daughters are affected if father is affected with a disease. If mother is affected there are only 50% chance that the male will be affected.
Mitochondrial inheritance: mitochondrial disorders are transmitted only from mother not from father. Both males and females are equally affected.