Ovarian CYST Management
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in or on the ovary. Ovarian cysts occur commonly in women of all ages. Some women with ovarian cysts have pain or pelvic pressure, while others have no symptoms.
Ovulation – “Functional” ovarian cysts develop when a follicle (sac) grows, but does not rupture to release the egg. These cysts usually resolve without treatment.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) – Women with PCOS may have many small cysts. These cysts do not need to be removed or treated with medication, but women with PCOS may need treatment for other PCOS problems, such as irregular menstrual periods.
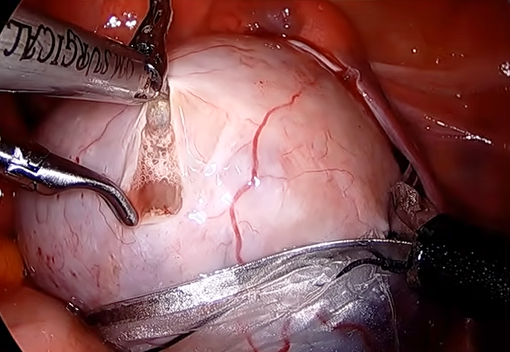
Endometriosis – Women with endometriosis can develop a type of ovarian cyst called an endometrioma, or “chocolate cyst.” These are recurrent and can cause fertility issues.
Dermoid cysts – Dermoid cysts (teratomas) are one of the most common types of cysts found in women. Torsion is one complication of ovarian cysts. Ovarian cysts can be detected during a pelvic ultrasound, CT Scan or MRI. Whether the surgery involves removing only the cyst or the entire ovary depends upon age and what is found during the procedure. It is ideal to discuss fertility preservation with an infertility specialist before any surgical intervention for ovarian cysts.
