Assessing Oocyte Quality: A Comprehensive Guide for IVF Practitioners
In the intricate field of in vitro fertilization (IVF), the quality of oocytes plays a pivotal role in determining the success of fertilization and subsequent embryo development. Understanding the subtle nuances of oocyte morphology and its implications on IVF outcomes is paramount for clinicians and embryologists. This essay delves into the critical factors of oocyte quality, emphasizing the importance of a meticulous assessment for informed decision-making in IVF laboratories.
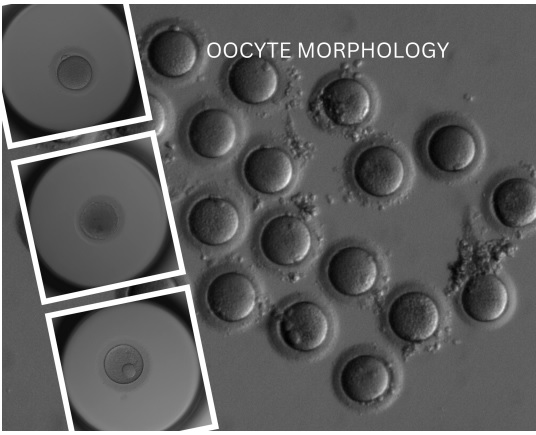
– Dr. G. A. Ramaraju DNB PhD, Consultant Krishna IVF Clinic
Granular Oocyte: A Marker of Oocyte Health
A granular oocyte, characterized by the presence of granules within the cytoplasm, often reflects the physiological or pathological state of the egg cell. The granularity of an oocyte is not merely a visual attribute but a significant factor influencing fertilization rates and embryo quality. Variations in granular appearance may signify distinct developmental competencies, necessitating a careful evaluation of these oocytes to determine their potential in IVF procedures./p>
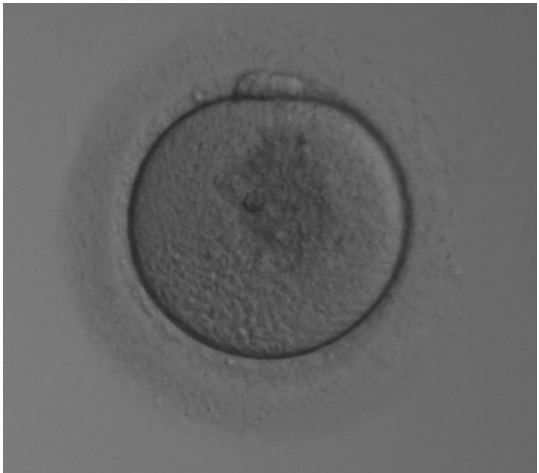
The Significance of Cytoplasmic Granularity
The granular appearance of the oocyte’s cytoplasm, indicative of the presence of proteins, mitochondria, or other organelles, serves as an essential metric for assessing oocyte health and maturity. While a moderate level of granularity is typical and expected, deviations in the pattern or intensity of granularity could signal underlying abnormalities. Recognizing these nuances is crucial in the IVF setting, where cytoplasmic granularity is a valued parameter for determining oocyte viability and potential.
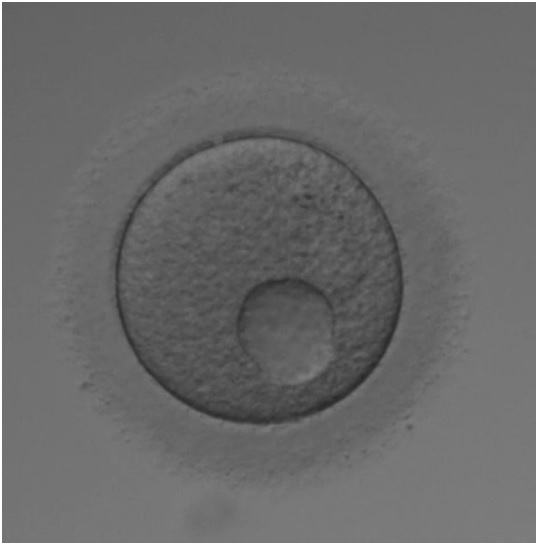
Egg Vacuoles: Indicators of Compromised Quality
Egg vacuoles, the clear, fluid-filled spaces within the oocyte’s cytoplasm, often emerge as red flags during the oocyte assessment. Their presence, typically attributed to factors such as aging, environmental stress, or metabolic imbalances, is generally viewed negatively. Vacuoles are considered markers of compromised ocyte quality, potentially leading to reduced fertilization potential and lower embryo quality. Their evaluation forms a critical part of the morphological assessment in IVF laboratories.
The Impact of Weak Oocyte Membrane
The integrity of the oocyte membrane, encompassing the zona pellucida and oolemma, is fundamental to successful fertilization and subsequent embryo protection. A weak membrane may impede sperm binding, elevate the risk of polyspermy, and ultimately compromise embryo viability. Given these implications, the strength and resilience of the oocyte membrane are meticulously assessed to ensure favorable IVF outcomes.

Large Oocyte: A Unique Consideration
Oocytes significantly exceeding the typical diameter range of 100 to 200 micrometers present a unique set of considerations. The enlarged size may reflect a distinct maturation stage or affect the distribution of vital organelles and molecules, influencing the fertilization process and embryonic development. Consequently, the size of the oocyte is a critical factor evaluated in conjunction with other morphological attributes.

The Role of Perivitelline Space in Oocyte Evaluation
The perivitelline space, the area between the oocyte’s plasma membrane and the zona pellucida, holds significant relevance in oocyte assessment. An unusually large perivitelline space may indicate aging or abnormal development, potentially affecting sperm penetration and fertilization. As such, this parameter is carefully considered in the morphological evaluation, contributing to the comprehensive assessment of oocyte quality.
Conclusion: The Art of Oocyte Assessment in IVF
In conclusion, the meticulous assessment of oocyte appearance and morphology is integral to gauging the health and potential of oocytes for successful fertilization and embryo development in IVF. Factors such as oocyte size, perivitelline space, granularity, membrane integrity, and the presence of vacuoles collectively contribute to a holistic evaluation. Given the substantial individual variations in oocyte morphology, each oocyte must be assessed on its entire profile, integrating continuous research findings to enrich our understanding of these factors. For clinicians and embryologists, this comprehensive evaluation is crucial for informed decision-making, ultimately shaping the success trajectories of IVF endeavors.
Fragmented polar body
A fragmented polar body in oocyte assessment is indicative of potential anomalies in oocyte maturation and subsequent embryonic development. Typically a byproduct of meiotic division, polar bodies should appear intact and well-defined. Fragmentation may suggest underlying chromosomal or cytoplasmic irregularities, potentially impacting the quality of the embryo post-fertilization. As such, careful observation and analysis of polar body morphology are crucial components in the embryologist’s toolkit for predicting IVF success and ensuring optimal selection of oocytes for fertilization.
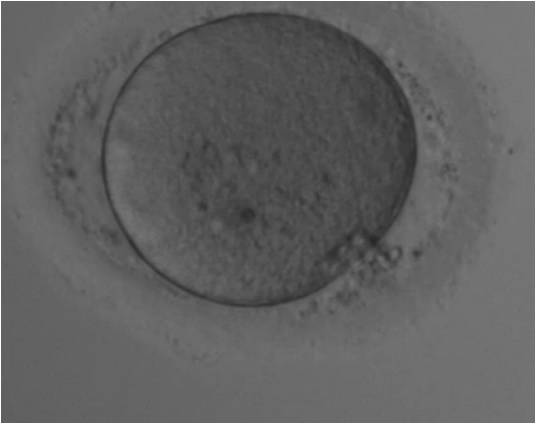
A Holistic Approach to Oocyte Assessment
In IVF laboratories, the evaluation of oocyte appearance and morphology is not just about ticking boxes. It’s a comprehensive analysis that provides insights into the oocyte’s health and its potential for successful fertilization and embryo development. Factors like oocyte size, perivitelline space, granularity, and membrane integrity are not just individual data points but pieces of a larger puzzle. As embryologists, we must consider these factors in conjunction with each other, recognizing that each oocyte presents a unique profile.
The field of assisted reproductive technology is ever-evolving, and as embryologists, our understanding of oocyte quality continues to deepen. By staying abreast of the latest research and continuously refining our assessment techniques, we can better navigate the complexities of oocyte evaluation, contributing to the success of IVF treatments and, ultimately, the journey towards parenthood for many.
Further reading:
- Cohen J, Schimmel M. The Oocyte: The Key to Embryo Quality. Unfortunately, I couldn’t find the specific publication details for this source.
- [Authors’ last names and initials]. Polar bodies in human oocytes: indicators of oocyte developmental competence. J Assist Reprod Genet. Unfortunately, the specific details for this source were also not available.
- Veeck LL. Oocyte assessment and biological performance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;541:259-74.
- Watson AJ. Cytoplasmic maturation of the oocyte: Its role in developmental competence and strategies for improvement in assisted reproductive technologies. Fertil Steril. 2007 Mar;85(13 Suppl):E1-3
