Imagine your gut as a bustling city, where trillions of microbes live in harmony, keeping the city’s defenses strong. This harmony is essential for your overall health, especially your immune system. But what happens when this balance is disrupted? Enter the concept of dysbiosis, and let’s explore how it affects your immune regulation and can even lead to autoimmune diseases and thyroid autoimmunity.
– Dr. G. A. Ramaraju DNB PhD, Consultant Krishna IVF Clinic
The Role of a Healthy Microbiota
Think of your gut microbiota as a well-organized orchestra. Each microbe plays a specific role, producing compounds that engage receptors on immune cells. These receptors, known as TLR (Toll-like receptors) and NLR (NOD-like receptors), trigger a cascade of immune responses. The result? The release of cytokines like TGF-beta, retinoic acid, and interleukins.
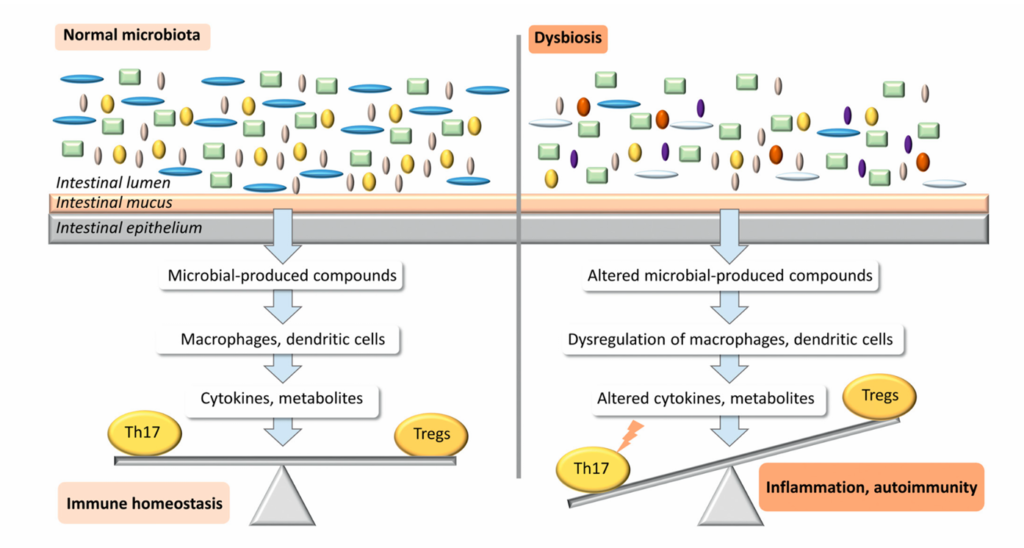
These cytokines are crucial for:
- Keeping a balance between pro-inflammatory Th17 cells and anti-inflammatory Tregs (regulatory T cells).
- Maintaining overall immune health.
The Chaos of Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis is like a city falling into chaos. This imbalance in your gut microbiota can wreak havoc on your immune system. Here’s how:
-
Disrupted TLR and NLR Signaling: Dysbiosis messes up the signals that keep your immune system in check. It throws off the balance between Th17 and Tregs.
- Increased Inflammation: With more pro-inflammatory Th17 cells and fewer anti-inflammatory Tregs, your body’s inflammation levels rise.
- Higher Risk of Autoimmune Diseases: This inflammation can lead to autoimmune diseases like Autoimmune Thyroid Disease (AITD), where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues.
Conclusion
Your gut microbiota play a pivotal role in maintaining your immune system’s harmony. Dysbiosis disrupts this harmony, leading to increased inflammation and a higher risk of autoimmune diseases. So, the next time you hear about the importance of gut health, remember—it’s not just about digestion. It’s about keeping your entire immune system balanced and healthy.
Reference:
Bogusławska, J., Godlewska, M., Gajda, E., & Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. (2022). Cellular and molecular basis of thyroid autoimmunity. European Thyroid Journal, 11(1), e210024.
